Difference between revisions of "Lex Tutorial"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
* '''a.out''' is lexical analyzer that transforms an input stream into a '''sequence of tokens.''' <br> | * '''a.out''' is lexical analyzer that transforms an input stream into a '''sequence of tokens.''' <br> | ||
[[File:Lex.png|center| Running Lex Programs ]] | [[File:Lex.png|center| Running Lex Programs ]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===The Lex Format=== | ||
| + | A Lex program is separated into '''three sections''' by '''%% delimiters'''. The format of Lex source is as follows: | ||
| + | '''{ definitions } <br> | ||
| + | %% <br> | ||
| + | { rules } <br> | ||
| + | %% <br> | ||
| + | { user subroutines }''' | ||
Revision as of 01:04, 10 August 2020
Lex
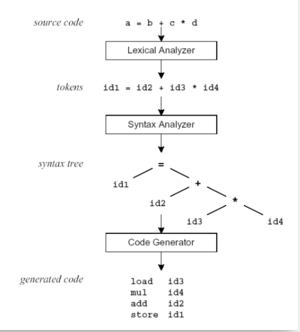
- Lex is a program that generates lexical analyzer. It is used with YACC parser generator.
- The lexical analyzer is a program that transforms an input stream into a sequence of tokens.
- It reads the input stream and produces the source code as output through implementing the lexical analyzer in the C program.
The function of Lex is as follows:
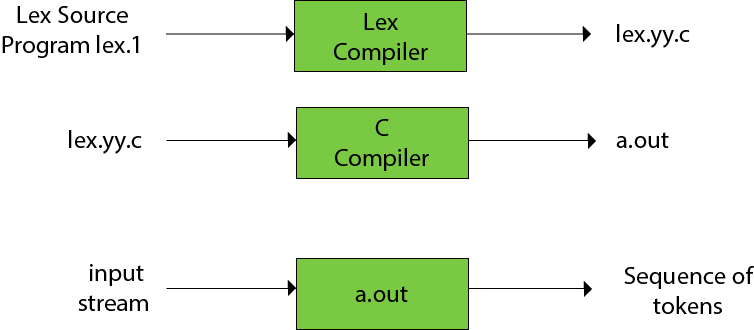
- Firstly lexical analyzer creates a program lex.1 in the Lex language. Then Lex compiler runs the lex.1 program and produces a C program lex.yy.c.
- Finally C compiler runs the lex.yy.c program and produces an object program a.out.
- a.out is lexical analyzer that transforms an input stream into a sequence of tokens.
The Lex Format
A Lex program is separated into three sections by %% delimiters. The format of Lex source is as follows:
{ definitions }
%%
{ rules }
%%
{ user subroutines }