Difference between revisions of "MPLab1 Addition"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
* Specify the size for code, data, and stack segments | * Specify the size for code, data, and stack segments | ||
''' .model small <br> .stack 100H ''' | ''' .model small <br> .stack 100H ''' | ||
| − | * | + | * Define your data in the data section ( here you can define various data items: '''variables, constants, strings, arrays''' |
| − | + | '''data1 dd 00H | |
| + | num1 db 10,13,"Enter the first number: $" | ||
| + | num2 db 10,13,"Enter the second number: $" | ||
| + | sum db 10,13,"The sum is :$" ''' | ||
==The function of Lex is as follows:== | ==The function of Lex is as follows:== | ||
Revision as of 22:55, 17 September 2023
32-bit Binary Addition Step by Step
- Specify the size for code, data, and stack segments
.model small
.stack 100H
- Define your data in the data section ( here you can define various data items: variables, constants, strings, arrays
data1 dd 00H
num1 db 10,13,"Enter the first number: $" num2 db 10,13,"Enter the second number: $" sum db 10,13,"The sum is :$"
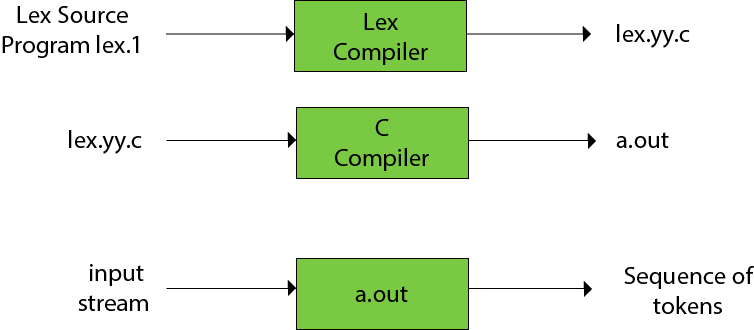
The function of Lex is as follows:
- Firstly lexical analyzer creates a program lex.l in the Lex language. Then Lex compiler runs the lex.l program and produces a C program lex.yy.c.
- Finally C compiler runs the lex.yy.c program and produces an object program a.out.
- a.out is lexical analyzer that transforms an input stream into a sequence of tokens.
The Lex Format
A Lex program is separated into three sections by %% delimiters. The format of Lex source is as follows:
{ definitions }
%%
{ rules }
%%
{ user subroutines }
Here
- Definitions include declarations of constant, variable and regular definitions.
- Rules define the statement of form p1 {action1} p2 {action2}....pn {action}. Where pi describes the regular expression and action1 describes the actions what action the lexical analyzer should take when pattern pi matches a lexeme.
- User subroutines are auxiliary procedures needed by the actions. The subroutine can be loaded with the lexical analyzer and compiled separately.
1. web: https://www.epaperpress.com/lexandyacc/index.html [ LEX & YACC TUTORIAL by Tom Niemann ]
2. web: https://www.javatpoint.com/lex