MPLab1 Addition
32-bit Binary Addition Step by Step
1. Specify the memory model for code, data, and stack segments
.model small .stack 100H
2. Define your data in the data section ( here you can define various data items: variables, constants, strings, arrays)
.data ; .data directive indicates the beginning of data section data1 dd 00H num1 db 10,13,"Enter the first number: $" num2 db 10,13,"Enter the second number: $" sum db 10,13,"The sum is :$"
3. Define your instruction in the code section (here you write the assembly instructions that perform computations, control program flow, and interact with data variables and memory)
.code ; .code directive indicates the beginning of code section .startup ; the entry point of the program MOV EBX, 00000000
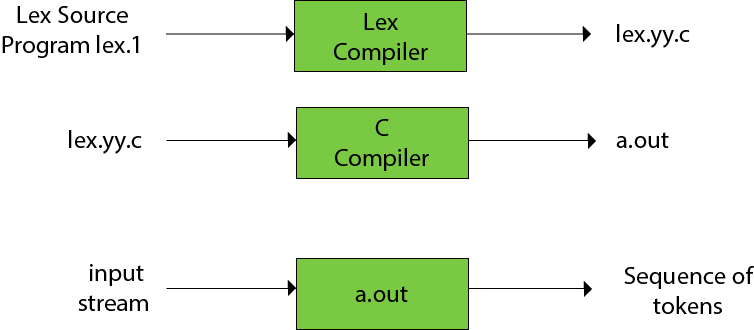
The function of Lex is as follows:
- Firstly lexical analyzer creates a program lex.l in the Lex language. Then Lex compiler runs the lex.l program and produces a C program lex.yy.c.
- Finally C compiler runs the lex.yy.c program and produces an object program a.out.
- a.out is lexical analyzer that transforms an input stream into a sequence of tokens.
The Assembly Program Structure
An assembly program is separated into three sections as follows:
.MODEL SMALL .STACK 100h
.DATA ;data definition go here
.CODE ;instructions go here